Candida is the most common type of yeast responsible for various yeast infections. Candidiasis is a type of yeast infection caused by Candida albicans. It normally lives on the skin and in the human body. It does not cause any problem if it is present in a small amount.
Certain conditions favor the growth of Candida and enhance its proliferation rate. These conditions create an environment where yeast can grow and multiply rigorously. As a result, the overgrowth of yeast leads to an infection. These infections can occur almost anywhere in or on the body, including the mouth, throat, skin, and genitals.
Types of Yeast Infections
There are different yeast infections depending on the type of yeast and the site where they are located. These infections can be treated easily with prescribed medications as per your healthcare professional.
The most common yeast infections are
-
Oral Yeast Infections
-
Cutaneous Candidiasis
-
Genital Yeast Infections
-
Invasive Yeast Infections
Recurrent yeast infections are typically mild and rarely cause severe complications. However, they can spread to other parts of the body and can potentially cause severe health problems.
① Oral Yeast Infections
Oral candidiasis is the condition in which yeast accumulates in the lining of the oral cavity, and it results in the spread of yeast infection in the mouth and throat. It is also known as oropharyngeal candidiasis, oral thrush, or simply thrush. Such types of yeast infections are common in infants and individuals with weak immune systems.
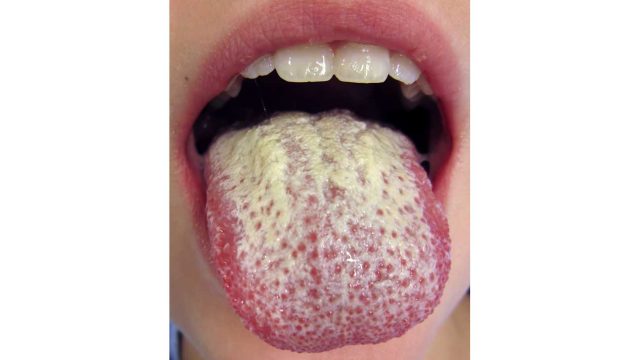
Oral yeast infections are common in newborns and are characterized by the appearance of yellowish or white lesions on the tongue and inner cheeks. Sometimes, these infections may spread to gums, the roof of the mouth, or the throat.
Candida may spread to the esophagus, resulting in a yeast infection known as Candida esophagitis or esophageal candidiasis. Such types of infections are common in people suffering from immune-compromised conditions such as AIDs.
⫸ Symptoms
Mild oral thrush may not develop notable signs and symptoms at first. If the infection persists, you may develop one or more of the following symptoms:
- Loss of taste
- Yellow or white lesions on tongue, gums, inner cheeks, or lips
- Dry and cracked skin at the corners of the mouth
- Irritation, soreness, and pain under dentures
- Bleeding, in case of severe infection
- Cotton-like feeling in your mouth
In severe cases, the yeast infection spreads to the esophagus and may develop worse symptoms, including:
- Fever
- Difficulty swallowing
- Feeling like food is stuck in your throat
As oral yeast infections are common in infants, they may spread the infection to their mothers during breast-feeding, and then the mother may experience specific symptoms, including:
- Cracked, red, or itchy nipples
- Pain in nipples while feeding
- Stabbing pain in the chest area
⫸ Causes
Oral yeast infections commonly occur in people who are:
- Wearing dentures
- Taking medications such as antibiotics and corticosteroids
- Diabetics
- Weak immune system due to HIV/AIDS
⫸ Treatment
Oral yeast infections are easy to treat. Treatment involves the intake of drugs for several days. In the case of immune-compromised patients, oral thrush is difficult to treat. Healthcare professionals usually treat yeast infections with antifungal drugs. Antifungal drugs are used to overcome and inhibit the growth of infectious yeast in your mouth and throat.
Antifungal drugs come in various forms that are easy to take for oral thrush, such as lozenges, syrups, and tablets. Your healthcare professional may prescribe amphotericin B, clotrimazole, itraconazole, and nystatin (antifungal mouthwash).
⫸ Prevention
You can prevent oral yeast infections by avoiding and adapting several habits. These are:
- Practice good oral hygiene
- Brush your teeth twice a day, especially before sleeping
- Use a medicated mouth wash to avoid yeast accumulation
- Keep your dentures clean after eating
- Remove your dentures before sleeping
- Eat healthy foods to strengthen your immunity
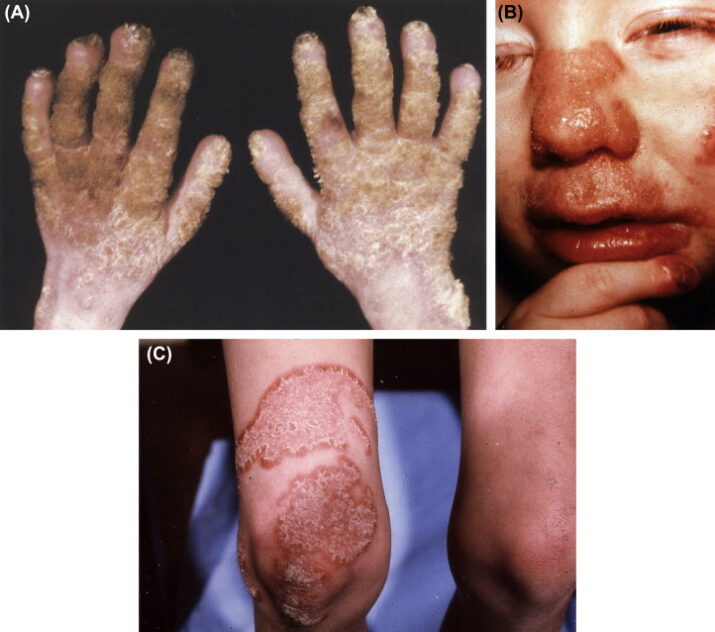
② Cutaneous Candidiasis
Cutaneous candidiasis, a skin infection generally caused by the yeast Candida albicans, can be acute or chronic. In cutaneous candidiasis, Candida infects the mucous membrane and superficial skin. These infections are common in parts of your body that trap moisture and heat, such as the armpits and the groin. They are more likely to happen in obese people with many skin folds where yeast can accumulate and grow in a moist environment.
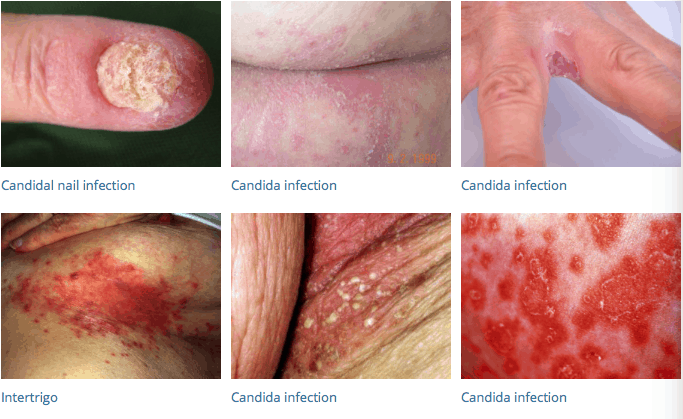
Cutaneous candidiasis occurs in the form of Diaper rash in babies. It is usually caused by leaving wet diapers on for too long. If the diaper is not changed after 3-4 hours, it will create a moist and damp environment that favors the overgrowth of yeast.
⫸ Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of skin yeast infection include:
- Itching
- Pustules
- Rash with redness
- Blisters
- Cracked skin
⫸ Causes
Skin yeast infections mainly occur in people with:
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Using antibiotics
- Weaken Immune System
- Poor hygiene
- Tight clothing
- Damp skin
- Warm environment
⫸ Treatment
Treatment of infection depends on the type of yeast infection and the site of infection. Skin yeast infections are treatable. Healthcare professionals may prescribe antifungal creams or powders to apply to the infected area. Usually, skin infections go away within 3-5 days, and your skin becomes rash-free.
⫸ Prevention
You can prevent skin yeast infections by avoiding and adapting several habits. These are:
- Good hygiene
- Change wet diaper or clothes immediately
- Avoid tight-fitting clothes
- Keep your skin dry and moisture-free
- Change damp socks and undergarments regularly
③ Genital Yeast Infections
Male and female genital yeast infections are:
Vaginal Yeast Infections
A vaginal yeast infection is characterized by burning and itching in the vagina, causing severe redness in the infected area and a white discharge from the vagina and vulva. The vulva is the tissue at the vaginal opening. These infections are caused by a fungal body yeast called Candida that is already present in your body.
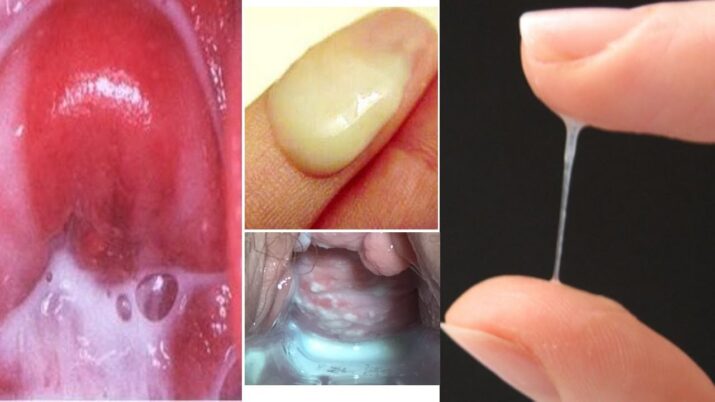
Yeast is a fungal type, and Candida is a particular yeast type that causes vaginal infections. When this yeast is harmonized with your body’s ecosystem, it doesn’t cause any problems. But when this equilibrium is disrupted, you can acquire a yeast infection that can proliferate.
Yeast infections of the vagina are not considered sexually transmitted infections. Instead, sexual contact can spread it. But women who are not sexually active can also suffer from this infection. There is an increased chance of vaginal yeast infections once someone becomes sexually active.
A healthy vagina contains some yeast cells and bacteria. However, the yeast cells can increase when the proportion of bacteria and yeast changes, leading to an infection that causes extreme itching, swelling, and irritation. These infections are very uncomfortable yet common. Throughout your life, you may experience such infections several times.
Vaginitis can be of numerous types, each with comparable symptoms. The most common symptoms are swelling of the vagina with painful discharge.
Drugs can effectively cure vaginal yeast infections. However, you might require a longer treatment course and a maintenance plan if you have repeated yeast infections – four or more within one year.
⫸ Symptoms
Symptoms of vaginal yeast infection range from mild to severe and include:
- Vaginal itching and irritation
- Vaginal and vulva soreness
- A sensation of burning during urination or intercourse
- Vaginal pain and rash
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Redness and swelling of the vagina
Some women can develop severe infections leading to swelling and cracks in the wall of the vagina. This may directly affect how severe your symptoms are, as long as your yeast infection remains untreated.
If you have any of these symptoms, contact your healthcare professional. The symptoms are similar to those of other forms of vaginal infections treated with various types of drugs.
⫸ Causes
The fungus Candida albicans is responsible for most vaginal yeast infections. The Candida fungus is an organism that occurs naturally in the vaginal area. The growth of this fungus is controlled by the bacteria Lactobacillus. The imbalance of these bacteria will assist the overgrowth of Candida that further leads to vaginal yeast infections.
Several factors can cause a yeast infection, including:
- Use of several antibiotics, which disturb natural vaginal flora
- Weak immune system
- Pregnancy
- Diabetes
- Stress
- Hormonal therapy leading to estrogen imbalance
⫸ Treatment
Vaginal yeast infections are treatable. Treatment involves the intake of drugs for several days. There are different types of yeast infections. Only your healthcare professional can prescribe your treatment depending upon the type of infection. Healthcare professionals usually treat vaginal yeast infections with antifungal medicines. This type of medication is used to overcome and inhibit the growth of infectious yeast in the body.
The two most common methods for vaginal yeast infection treatments are the oral method and the topical method. In the Oral method, medication is taken by mouth. In the topical method, medication is applied to the infected area. The topical method includes medications like boric acid, miconazole, nystatin, etc.
Your healthcare professional may provide you with proper guidelines on how each medication is to be used correctly. It is crucial to carefully follow your provider’s directions to ensure the infection is fully resolved and does not come back.
⫸ Prevention
You can prevent vaginal yeast infections by avoiding and adapting several habits. These habits are:
- Avoid tight-fitting underwear
- Avoid douching, which removes helpful bacteria from the vagina that prevents infection
- Avoiding the use of scented feminine products
- Avoiding hot tubs
- Avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics
- By wearing cotton crotch underwear
- Eating a balanced diet
- Improving your sleep cycle
- Adapting hygienic ways to avoid infection growth
- Eating yogurt and Lactobacillus supplements
Yeast Infections in Men
Although vaginal yeast infections are more common, yeast infections may also be common for men. These are known as a penile yeast infection when it affects the penis. If not treated, penile yeast infection may develop various symptoms, which are unpleasant, uncomfortable, and perhaps unsightly. If your infection spreads in your bloodstream, it may also lead to severe consequences.
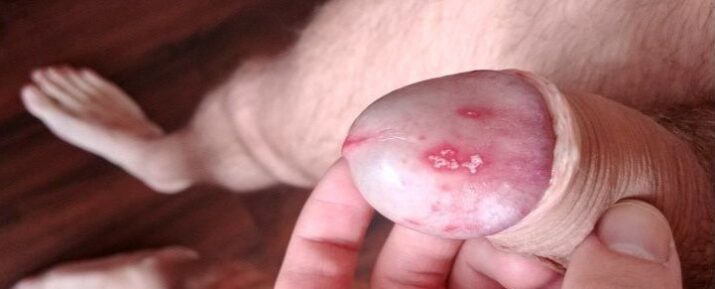
⫸ Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of penile yeast infection may not be so evident. However, you may have:
- Redness
- White patches
- Burning and itchy sensation on the penis
⫸ Causes and Prevention
Candida is not just present on the female body, but all bodies, which can lead to yeast infection if there is an excess of this fungus. Due to warm skin and wetness, the groin area is particularly vulnerable to Candida growth.
However, the most common reason for penile yeast infections is unprotected vaginal relationships with a woman who has the condition. By wearing condoms during sex, you can help avoid a yeast infection. It also helps to bathe regularly.
④ Invasive Yeast Infections
Invasive candidiasis infection is an infection caused by yeast, a type of fungus called Candida. Invasive candidiasis is a severe illness that can impact the blood, heart, brain, eyes, bones, and other body parts. Unlike Candida infections in the mouth, throat, and vagina, Invasive candidiasis is a severe infection that can cause chronic complications.
Candida usually lives inside the body and on the skin without causing any infection. However, in patients who are at risk, Candida can enter the bloodstream and cause infection. Candidemia, a bloodstream invasive candida infection, is a common infection in individuals admitted to hospitals.
⫸ Symptoms
Fever and chills that are not improving after antibiotic treatment for suspected bacterial infections are the most prevalent symptoms of invasive candidiasis.
Similar symptoms may occur when the infection reaches other body regions, including the heart, brain, eyes, bones, or joints.
⫸ Treatment
Antifungal medications are used to treat invasive yeast infections. Medication use depends upon the patient’s immune system, age, and severity of invasive candida infection. For adults, the initial treatment involves the intake of antifungal drugs like micafungin or caspofungin, fluconazole, and amphotericin B. These antifungal medications are most suitable for treating invasive yeast infections. The treatment should continue for two weeks or until symptoms are resolved, and candida yeasts are no longer in the bloodstream.
The post Types of Yeast Infections and How to Treat Them appeared first on Dumb Little Man.
0 Commentaires